Want to Extend Your Working Years? Try Switching Jobs
Alicia H. Munnell is a columnist for MarketWatch and senior advisor of the Center for Retirement Research at Boston College.
Why a late-career job switch could be a good move.
It always surprises me that older workers are willing to hurl themselves onto the job market. Yet, voluntary job-changing among late-career workers increased steadily between the 1980s and the mid-2000s before declining somewhat in recent years. Today, more than 40 percent of workers 58-62 have voluntarily changed jobs after age 50. In an era when many workers have to work longer, an important question is whether changing jobs hurts or helps their prospects for remaining in the labor force.
The effect of voluntarily changing jobs on retirement timing is an open question. Research has shown that such job changers generally report greater job satisfaction, albeit with a decrease in compensation. Since workers presumably change employers to improve their well-being, moving to a job that they consider better could extend their careers. On the other hand, job-changing could reduce job security because tenure protects older workers against involuntary job loss, and workers who change jobs risk a bad match. Changing jobs thus could increase the risk of a layoff and an early labor force exit.
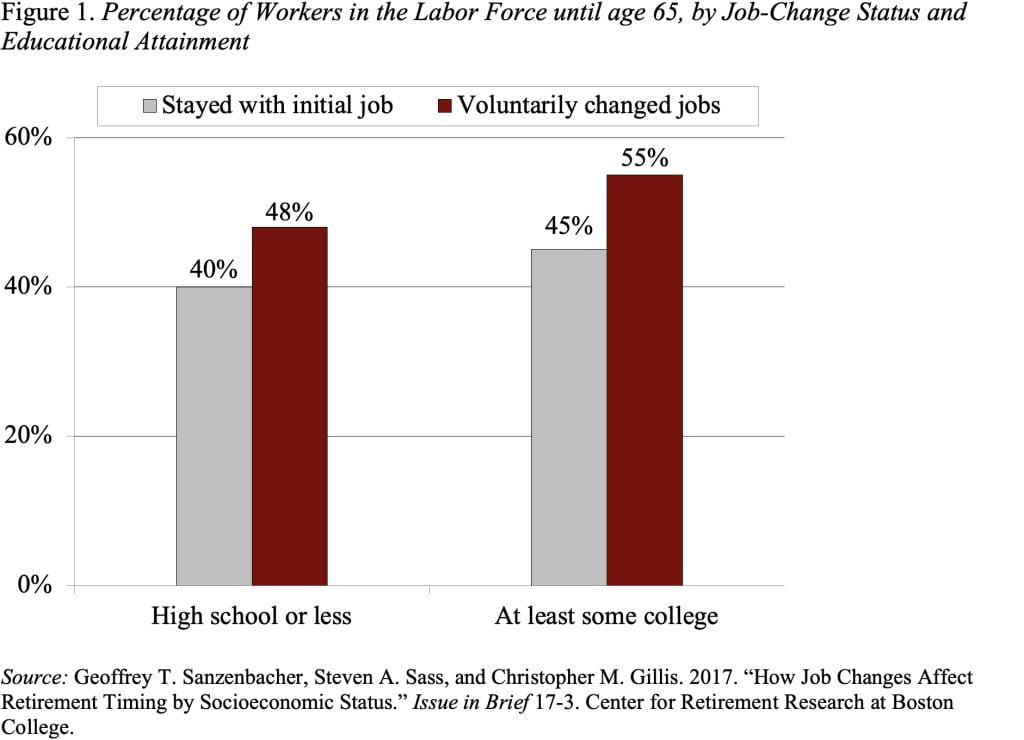
A simple tabulation of the data from the Health and Retirement Study shows that those who voluntarily changed jobs are more likely to remain in the labor force until age 65, with the difference slightly larger for better-educated workers (see Figure 1). But this pattern could reflect other things. For example, people who switch jobs could be in better health, so better health – not the job change – could be the reason they work longer. Thus, it’s important to control for other factors to isolate the impact of job change on retirement.
The results of a regression – controlling for factors such as health, the nature of the job (blue-collar/white-collar), coverage under a defined benefit plan, planned retirement age, and homeownership – show that the effect of voluntary job-changing on being in the labor force at age 65 is large and statistically significant; and this result holds for both educational groups. Workers with at least some college who voluntarily changed jobs were 10.9 percentage points more likely to be in the labor force until age 65. For less-educated workers, the effect was 7.5 percentage points. That is, the results controlling for other factors are very similar to those from the simple tabulation of the data.
Changing employers involves risks and not all older workers can move to a better job. But for those who can, a voluntary job-change is associated with a large and statistically significant increase in the likelihood of remaining in the labor force to age 65.






